The History of Artificial Intelligence
Not very far in the past, Artificial Intelligence seemed a distant dream. Today, it’s pretty much everywhere, even though in its weakest forms. The AI industry is now worth $327.5 billion and is expected to grow up to $500 billion by 2024, according to a report by International Data Corporation (IDC). Though, the history of artificial intelligence is longer than we can imagine.
Artificial Intelligence is defined as the development of a computer system that is able to perform a task that requires human intelligence, for example, speech recognition, visual perception, decision making, and translation between languages. A more lucid definition would be “the intelligence exhibited by machines or software”. It also refers to the academic field of study, which studies how to create computers and computer software capable of intelligent behavior. Since there is no clear line between ordinary software and AI, it becomes difficult to distinguish the difference. Hence, one may think of AI technology as the sort of technology one would use to perform tasks that require some level of intelligence to accomplish.
The long-term goal of AI research ever since its inception has been what is called Strong AI, which describes a computer capable of doing every intelligent task that a human can perform. However, presently the AI innovation no more relies upon whether we accomplish Strong AI or not. The technology has now progressed to a level where, regardless of future advancements in the field, it is poised to disrupt any innovation-based industry.

The origins of Artificial Intelligence
Before we go ahead, let us try to trace the origins of Artificial Intelligence in its insatiable quest.
All through mankind’s history, individuals have utilized technology to model themselves. Each new technology has been the base for an advanced model of the mind. The history of artificial intelligence dates back to about 400 years ago when people started to write about the nature of thought and reason. In 1985, Haugeland described Hobbes (1588-1679) as the “Grandfather of AI,” who believed that tasks such as writing using paper and pen or talking out loud involved symbolic reasoning. Descartes (1596-1650), Pascal (1623-1662), Spinoza (1632-1677), Leibniz (1646-1716), and other pioneers in the philosophy of mind further developed the idea of symbolic reasoning.
With the development of computers, the idea of symbolic operations became more solid. Charles Babbage (1971-1871) designed an Analytical Engine which was the first general-purpose computer, which was not built until 1991.

In the early 20th century, the basics of modern computation were being developed by scientific researchers. Several models were proposed, such as the Turing Machine, a theoretical machine that was able to write symbols on the infinitely long tape. This was developed by Alan Turing (1912-1954).
Early AI programs
The development of real computers with some of their applications as AI programs included a large number of low-level learning inspired by neurons.

These early programs concentrated on learning and searching as the foundations of the field. It became evident early that one of the primary issues was introducing the necessary knowledge to tackle a problem. For the learned knowledge, the agent must have a proper target language before learning. In the following years, the AI community progressed through these stages:
- 1960s and 1970s – Scientists successfully built systems in limited domains which were capable of understanding natural language.
- 1970s and 1980s – Researchers started the development of expert systems to train computers in order to perform expert tasks.
- 1980s and 1990s – Expansion of neural networks and behavior-based robotics.
- 1990s and 2000s – Sub-disciplines of perception, probabilistic and decision-theoretic reasoning, planning, embodied systems, machine learning progress significantly.
- 2000s and 2010s – Autonomous vehicles, optical image recognition, and virtual assistants become more popularized.
- 2020s and beyond – AI-assisted surgeries and virtual nurses, robotic inclusions in industries such as retail, manufacturing, etc., quantum computing with AI and machine learning.
However, AI has seen many highs and lows during the phase of development. And yet, it has always survived through its “winters” over the course of time.
Returning interest in AI technology
AI appears to be entering a new phase where interest is re-surging. An example of commercial usage of AI is IBM’s Watson, a distributed cognitive framework that is deployed on the cloud. The system becomes better by collecting every piece of information while it is being used by people. Although a few things have changed to advance this surging interest in AI, these are the essential factors responsible:
- The cost of computing power has declined drastically
- The power of computing has improved exponentially
- The data availability has increased manifold
- The core algorithms within the systems have evolved substantially
The mix of the four elements sketched out above is making applications — which have a tendency of consuming massive amounts of computational power and information — more pragmatic.
AI’s place in the business world 2021
In reasonable terms, this has implied that computations that used to take up to a few weeks now take less than a day. And the time is contracting. Social networks, mobile phones, and the emergence of wearable consumer devices have created an explosion of data needed to feed the data-hungry AI engines and, in turn, enable them to operate at peak performance. Besides, this data explosion is so vast and overpowering that it has become difficult to comprehend it without smart computerized support.
AI plays a vital role in improving business processes, such as:
- AI with Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Repetitive and high-volume tasks can be organized and performed.
- Better marketing results: From competitive analysis to building a comprehensive sales process. Tracking the user journey and making recommendations accordingly.
- Finance and accounting: Finance industry has many rule-based, repetitive tasks which can be handled using machine learning techniques.
- Enhanced retail management: Improved and efficient billing, supply, and inventory management.
- Improved customer service: Voice recorded responses, or IVR can provide customer service with pre-set rules and data, reducing the manpower and time consumed.
- Prediction of behavior: Machine learning and artificial intelligence can predict the behavior of users and offer them custom solutions according to their needs.
Advances in analytics, especially progress in machine learning with the needed computational power now available to support them, make the modern systems more versatile and less demanding to create and actualize. Finally, despite its “winters,” the innovation base has kept on evolving and growing exponentially (but discreetly), with every development surpassing the former.
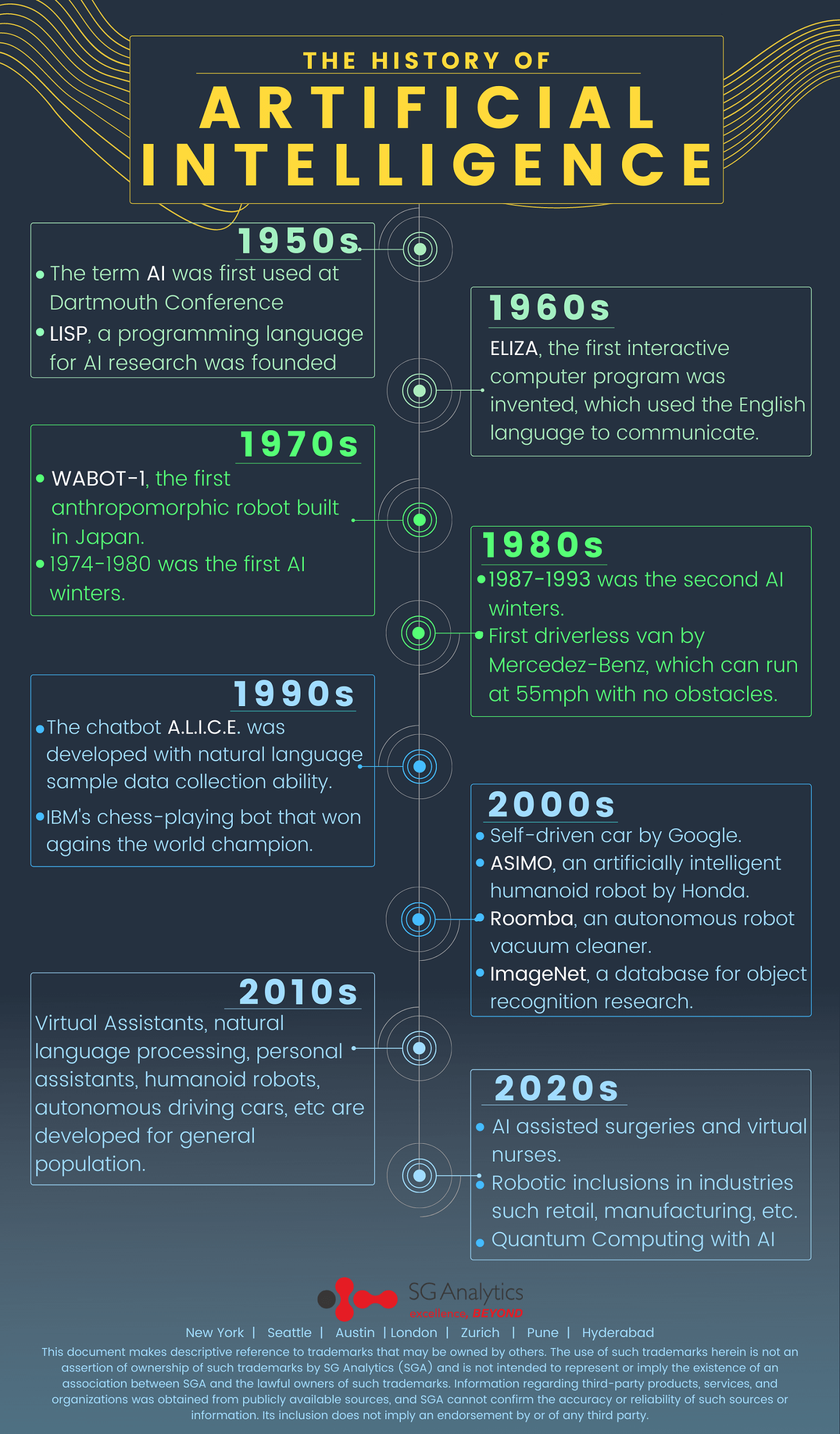
The timeline beyond 2022
AI has the power to disrupt every industry, with innovations such as applied natural language processing, auto-driving vehicles, quantum computing, auto-regressive language models such as GPT 3, and so on. The history of artificial intelligence describes the innovation and possibilities it has to offer.