With the market power of technology on the rise, organizations are exploring and identifying how technology and intangible assets are changing the global economy. The biggest contrast between the industrial revolution and the technology revolution lies in the assets and wealth derived from them. While the technological revolution is critically different, a qualitative assessment enables organizations to establish a relationship between the financial and economic qualitative underpinnings of the view.
It is vital to recognize the pattern of the diffusion of technology with a focus on the current monopoly practices. Modern technology is driven majorly by the faster adoption of automation software. While monopoly wealth is considered as an intangible asset basis, the monopoly advantage is derived from intangible assets and the acquisition of smaller companies.
How have technological changes accelerated and made suggestions for organizations to address the evolving landscape?
Today the cumulative advantages of the global economy are directly related to technology firms. A fast follower examines the market to identify what’s succeeded and repeats it. Understanding the components that work makes R&D faster and less expensive. In fact, the strong point is that acquisition stunts innovation, and competition is one of the significant examples of the fast-follower methodology.

Read more: Artificial Intelligence and the Downsides of AI Data Collection
Understanding the Economic Benefits and Implications of Technology
Today the mood is shifting when it comes to technological innovation. Recent pessimism around the growing pace of innovation is turning into optimism. However, some concern still exists. The speed of innovation is predominantly driving this change that the pandemic spawned. Scientists invented COVID-19 vaccines at a prominent speed, workers shifted to digital technologies to accomplish their jobs, and people started adopting digital payments; these are some of the other technological advances made over the past few years.
While some professions are likely to disappear with increased automation, technology could also pave the way for better-paid and more valuable jobs. With mountains of research, knowledge, and experience at our disposal, organizations are now ensuring that the new industrial revolution will be an equitable and sustainable one.
The digitally enabled revolution is advancing faster, leading to a period of innovation. Rapid advances in technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, the internet of things (IoT), nanotechnology, and biotechnology are emerging as the bedrock of this wave of innovation. To further ease the growing concerns among workers, the private and public sectors are exploring opportunities to work in close collaboration with skilled investment firms to upskill their staff and employ these new technology tools. Technology is providing easy access to a wider pool of talent because remote working is breaking down geographical barriers. And even for employees, these new tools provide an opportunity to grow and develop their skill sets.
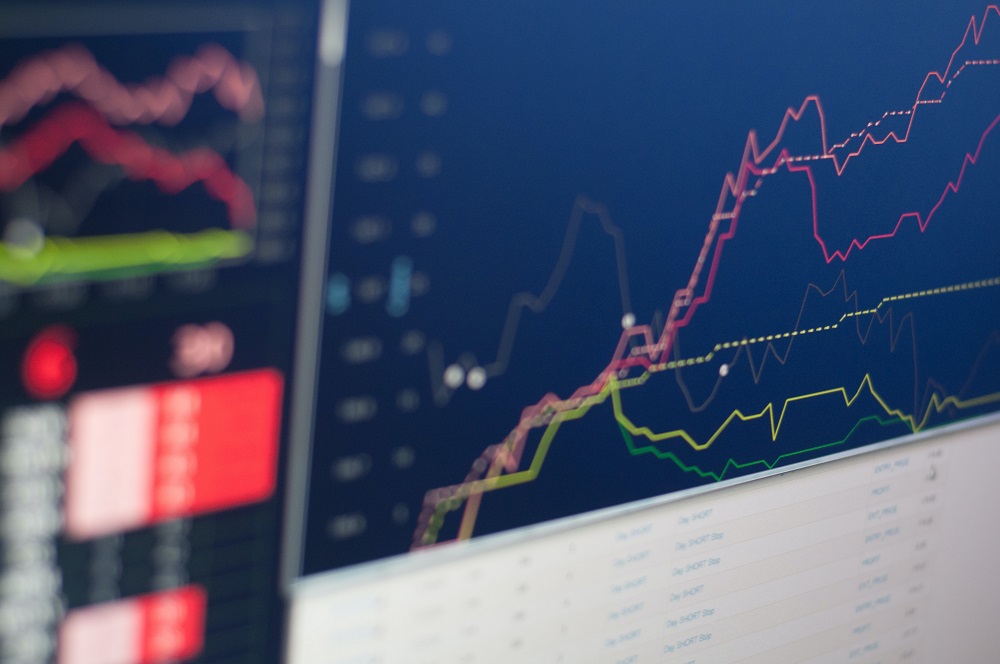
Read more: The New Buzz in Town: What is ChatGPT and Why Has it Taken the World by Storm?
Adopt but also Adapt to the Transition
In a recent report, PwC identified ten emerging technologies. The list includes synthetic biology, advanced materials, 3D printing, robots, and artificial intelligence. Organizations across the globe now, individually, and collectively, are integrating these advancements to experience the greatest advancements and fostering an environment that aligns with their sustainable development goals. The report also pointed out some significant examples of emerging applications that are finding use across different industries, including energy.
One of the core innovation challenges lies in the fact that to achieve these technological breakthroughs; organizations need to be able to create a next-generation clean distributed framework that will help in aggregating the emerging resources that will be optimized by AI and machine learning, along with blockchain and IoT-enabled trading.
The application of complex tools helps in studying the different facets of the economy, thereby enabling businesses to identify and analyze existing traditional tools and initiate a transition to a more advanced ecosystem. The absence of these tools has managed to work with low-dimensional representations of reality. But with the increasing availability of detailed insights into social phenomena, organizations can make it particularly useful to employ new tools to exploit this informational richness. This is opening fascinating new horizons across all fields of knowledge.
Across the globe, technology lies at the core of the economic growth of countries. Technological advancements are allowing for more efficient production of better goods and services, leading to prosperity and growth. The mechanisms on which the innovations are developed, adopted, and used in production enable organizations to gain a detailed analysis and explore new findings that could likely impact many areas of research and development policies.

Read more: 21st Century Outlook: The Rise of Pragmatic Technology in Businesses
Productivity in the Digital Age
The digital revolution is being accepted and worked upon. At the same time, the earlier general-purpose technologies demonstrated that with short-term dislocations, organizations today are reorganizing the economic developments around revolutionary technologies to generate huge long-term benefits.
This digital transformation, over the years, has resulted from what economists call a general-purpose technology. It is the one that holds the power to continually transform itself while progressively branching out and boosting productivity across different sectors. While such transformations are rare, these changes bring along long-term benefits.
To analyze empirically the nature of the global ecosystem and partnerships that underpin technological progression and its manifestation in the evolution of new industries. Leading firms are now committing to their digital strategy and devoting sufficient resources as a core organizational priority. They are also mobilizing their organizational operations around their transformation by responsibility and ownership. They are designing a flexible and agile framework that focuses on continuous development and making bets to reinvent themselves.
To expand the dimensions of opportunities, organizations are employing quantitative tools to tap into their worldwide users, thereby allowing policymakers, corporations, and the broader public to benefit from the results. Technology has lifted productivity for major firms; however, the benefits have not been fully captured. By effectively collecting the benefits of today’s technologies, businesses can ensure that their dividends are spread economy-wide.
Read more: ChatGPT and Digital Transformation – A Leap in the Dark

Final Thoughts
Technology today has changed the way we innovate and connect. It has enabled organizations to create and test new innovations while reducing the costs and risks of product development. This success of the digital age is dependent on collaboration between the public and private sectors. Governments and industry regulators, however, must ensure that these regulations keep up with the growing pace of innovation to avoid monopolies and protect citizens.
With organizations adopting increasingly modern technologies into their everyday operations and enjoying the benefits of these, there is a looming fear over future jobs. However, the cusp of widespread change is making the future more hopeful.
The recent shift to integrate open innovation has encouraged organizations to increase their flows of knowledge and foster new types of cooperation between institutions and businesses. Top corporate investors globally are leading the development of many emerging technologies. This is evident from examining the technology fields in which these companies are intensifying their inventive activities. The constitution of top R&D investors to the overall development of these fields is also considerable. Top R&D investors are accelerating their inventive activities in diverse areas like automated driving systems, big data, artificial intelligence, and communication technologies.
With a presence in New York, San Francisco, Austin, Seattle, Toronto, London, Zurich, Pune, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics, a pioneer in Research and Analytics, offers tailor-made services to enterprises worldwide.
A leader in the Technology domain, SG Analytics partners with global technology enterprises across market research and scalable analytics. Contact us today if you are in search of combining market research, analytics, and technology capabilities to design compelling business outcomes driven by technology.