Green bonds are quickly gaining popularity as a way for businesses to raise funds for projects, assets, or other initiatives that support the economy, climate, or community. Governments have begun to foster the growth of the green bond market, and investors have flocked to ‘green’ investments, raising interest to new heights in the recent years.
To combat global warming, trillions of dollars would be required. Green bonds are a way for issuers to raise funds for environmentally friendly programmes like renewable energy or clean transportation while still being able to talk openly about it. The bonds are also appealing to fund managers since they view it as a way to satisfy growing investor demand for sustainable investments. The sector, which slowly started gaining momentum a decade ago, has recently exploded, and has aided in the growth of other debt-related socially conscious products.
Since it’s difficult for investors to tell if a bond is actually green, regulators put increased emphasis on standards to prevent greenwashing, or making false statements about how environmentally friendly an issuer is.
What are green bonds?
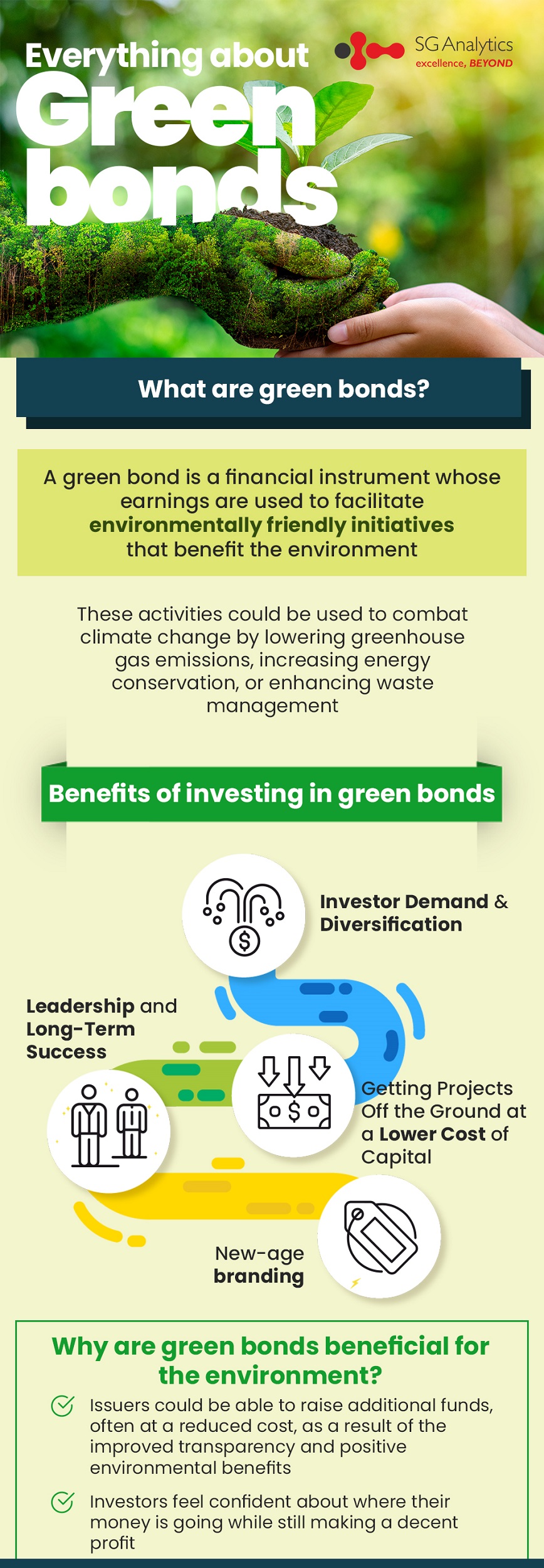
A green bond is a fixed-income security that is intended to fund particular climate or environment-related projects. Green bonds are typically accompanied by tax benefits that make them more appealing to investors. The first certified green bond was issued by the World Bank in 2009. A green bond is a financial instrument whose earnings are used to facilitate environmentally friendly initiatives that benefit the environment. These activities could be used to combat climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions, increasing energy conservation, or enhancing waste management.

The green bond market has exploded, with annual global issuance increasing more than double in the last five years. It requires a benchmark borrower to become a fully functioning asset class. That’s a job that the European Union is well positioned to perform by selling environmentally friendly debt as it ramps up its bond-issuing campaign to help the region recover from the pandemic.
The global green bond market is expected to rise to 1 trillion euros (US$1.22 trillion) in 2021, according to NN Investment Partners. The EU Taxonomy and EU Green Bond Standard, which derive from the European Union’s Sustainable Action Plan to fund sustainable economic development, are driving the growth of the market.

The creation of the first edition of the EU Taxonomy and EU Green Bond Standard will have a long-term positive effect on the EU green bond market’s credibility and transparency, and will serve as a framework for regulatory reform in other regions.
The new regulations will further centralize and formalize the green bond market which is maturing rapidly. It will also help raise awareness about the economic practices that are environmentally friendly and how businesses and investors can adapt them to become more sustainable. Additionally, it will provide investors with a more comprehensive analysis of their investments, allowing them to make more informed decisions.
Benefits of investing in green bonds
Green bonds offer investors the opportunity to gain tax-free income while also ensuring that their money is being put to good use. As the demand of Green bond keeps increasing, it correlates to lower borrowing rates. Lower borrowing costs mean lower expenses, which are either passed on to investors as a dividend or used to offset the operating costs of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or bonds. Here are some of the benefits of investing in green bonds: