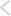Customer analytics became an important source of information in decision-making. One of its main benefits is to show the price sensitivity of customers towards a particular product, which can be seen by developing a price-elasticity model with sales revenue as the dependent variable and price as the major independent variable. This price-elasticity is usually a regression model, and it includes other independent variables (apart from price) representing one or some or all of the following:
- Store-specific information
- Demographic information
- Promotion and discount information
- Competitor details
- Cannibalization information
- Special events, festivals, and holidays
- Macroeconomic factors
Introduction to Price-Elasticity Regression
Price elasticity assists in measuring the responsiveness of the quantity demand or supply of goods to a change in price. It assists in measuring the relationship between a change in the quantity demanded and a change in its price.
It is used to identify the responsiveness of the quantity required of a good or service. Price elasticity is measured as the percentage change in the quantity of the demand/supply product divided by the percentage change in price. In marketing, elasticity helps in understanding how sensitive customers are to a change in the price of a product. Price elasticity analytics is a key element in setting prices that enables businesses to meet their goals.
Importance of Price Elasticity Model in Business Decision-making
The elasticity of demand implies the sensitivity of the quantity of a commodity in response to the change in factors. However, the elasticity of demand can be of different types based on factors that are responsible for driving the change in demand. The price elasticity of demand is a useful tool for making critical decisions, such as determining the price of goods and services.
Determination of price: The primary objective is to earn profit or increase revenue to maximize profits.
Monopoly in price determination: It presents a situation where a single group or an organization controls all of the markets for a particular good or service. However, the monopolistic market lacks competition.
Price determination under monopoly: The situation helps a single group or company to charge different prices for the same commodity at different markets.
In this way, the same product can be considered elastic in one market and inelastic in the other.
However, if a business is not leveraging price elasticity for informed pricing decisions, they are blindly navigating the landscape. It is, therefore, critical for businesses to study the elasticity depending on the market and make pricing decisions accordingly.
How to Tweak Variables?
Quite often, the price-elasticity model does not end up as a normal multivariate linear regression model. It requires understanding the relationship between sales and price, and tweaking the dependent variable of sales and the independent variable of price accordingly through variable transformation. There is a good reason for that, as there is empirical evidence that models with such transformed variables provide better accuracy and stand up to model diagnostics tests in a much more respectable manner. However, a discussion on empirical evidence is beyond the scope of this article.
Three types of transformations are definitely explored while constructing a price-elasticity model:
- Logarithmic transformation of a dependent variable (sales), no transformation of an independent variable (price) (Log-Linear Model)
- No transformation of a dependent variable (sales), logarithmic transformation of an independent variable (price) (Linear-Log Model)
- Logarithmic transformation of a dependent variable (sales), logarithmic transformation of an independent variable (price) (Log-Log Model)
Choosing the Right Regression Model
Thus, at least four kinds of regression models are explored: a normal regression model and a regression model for each of the three aforementioned transformations. More models can be explored by considering various transformations, but usually, these four different approaches should suffice for developing a price-elasticity model.
To choose the right approach, one needs to explore the relationship between the dependent and independent variables (Sales vs. Price). This can be done through simple graphical analysis or simple regression. The graphs for each of the four models are shown below:
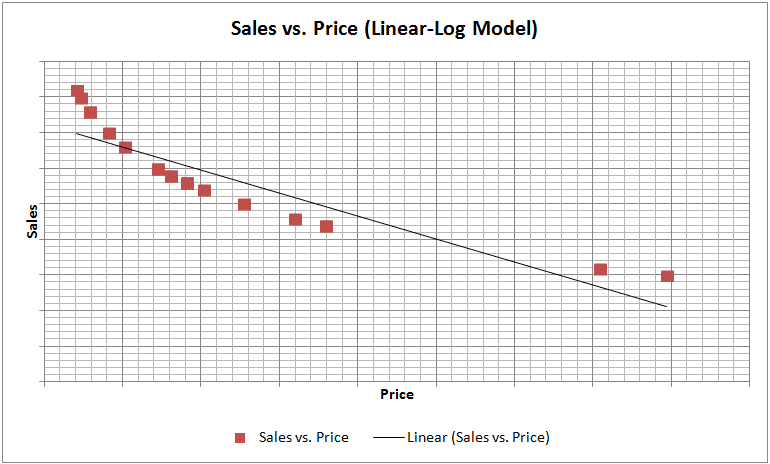
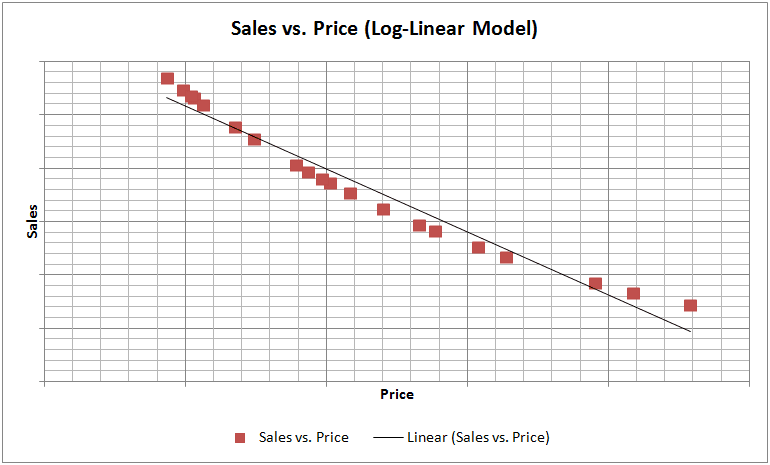
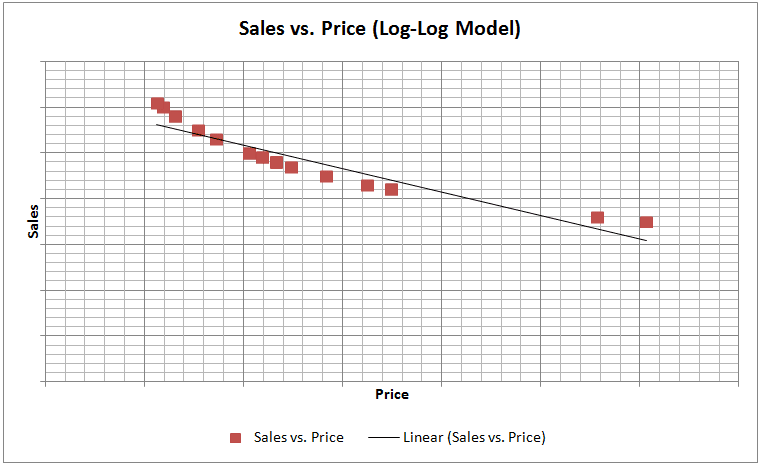
One of the main assumptions of linear regression is that the relationship between Y and X should be approximately linear. We can observe from the sample graphs above, that if the relationship between Y and X is of curvilinear nature, then it is definitely worthwhile to perform logarithmic transformations and check the linearity between transformed variables and select that transformation, which provides the best linear fit between Y and X. The curvilinear relationship between Sales and Price seems to be a general feature of economic reality and thus, logarithmic transformations tend to work well with these variables.
Read more: The 7 Biggest Technology Trends In 2022
Besides satisfying the linear regression assumption of linearity of dependent and independent variables, another reason for choosing logarithmic models is that these models are consistent with the “no money illusion” theory. “No money illusion” is a microeconomic theory, according to which, if there is an increase in income and prices to the same extent, then the quantity demanded of a product remains the same. However, this is a point of debate among economists. It is quite probable that in the short term, “money illusion” actually exists (due to lack of awareness and alertness related to the real and nominal value of goods and services) and it does have an impact on aggregate consumption. However, in the longer term, “money illusion” fades away resulting in “no money illusion” and aggregate demand returns to previous levels.
Read more: Top AI Trends to Watch Out for in 2022
Thus it can be concluded that to develop the right price-elasticity model, the relationship needs to be studied between sales and price and appropriate transformations, if required, need to be done on these variables. We also need to take into account other factors for model development. Lastly, the general state of economy needs to be studied in the present context (regarding the existence of “money illusion”) and the right model needs to be chosen.
Read more: Top ESG Investing Trends to Watch Out for in 2022
With offices in New York, Austin, Seattle, London, Zurich, Pune, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics is a leading research and analytics company that provides tailor-made insights to enterprises worldwide. If you are looking to make critical data-driven decisions, decisions that enable accelerated growth and breakthrough performance, contact us today.
With a presence in New York, San Francisco, Austin, Seattle, Toronto, London, Zurich, Pune, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics, a pioneer in Research and Analytics, offers tailor-made services to enterprises worldwide.
A leading enterprise in Data Analytics, SG Analytics focuses on leveraging data analytics, and data science to help businesses across industries to discover new insights and craft tailored growth strategies. Contact us today to make critical data-driven decisions, prompting accelerated business expansion and breakthrough performance.
About SG Analytics
SG Analytics is an industry-leading global insights and analytics firm providing data-centric research and contextual analytics services to its clients, including Fortune 500 companies, across BFSI, Technology, Media and entertainment, and Healthcare sectors. Established in 2007, SG Analytics is a Great Place to Work® (GPTW) certified company and has a team of over 1100 employees and has presence across the U.S.A, the U.K., Switzerland, Canada, and India.
Apart from being recognized by reputed firms such as Analytics India Magazine, Everest Group, and ISG, SG Analytics has been recently awarded as the top ESG consultancy of the year 2022 and Idea Awards 2023 by Entrepreneur India in the “Best Use of Data” category.
FAQs - Price-Elasticity Model
-
What is the significance of price elasticity in business?
Elasticity is a critical economic measure because it presents how a good or service is consumed by buyers when there is a price change. But when a product is elastic, this change in price results in a change in demand. It assists businesses in general in fixing the price.
-
How do you calculate price elasticity from regression results?
The demand price elasticity is measured as the percentage change in the demand with respect to a percent change in the price of the good.
-
Can price-elasticity regression be applied to service-based industries?
Price Elasticity of Demand or PED helps in predicting the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in its price. It is a powerful way to check how certain products are more sensitive to price changes than others. Price elasticity assists in identifying how sensitive the demand and supply of the product is.