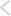The thought of a pollution-free and eco-friendly environment is the basis of reducing carbon footprint and emission of greenhouse gases. This paved the way for the replacement of coal and oil with natural gas and renewable energy sources for fuels.
What is Hydraulic Fracturing?
Hydraulic fracturing or fracking refers to the injection of water, various chemicals, and sand deep down the earth under high pressure to extract this natural gas from shale and other types of sedimentary rocks. The essential source for the fracking process is water and this process is also referred to as unconventional production.
Although fracking aids to extract natural gas, it comprises of restraints that may outweigh its significance. In this article let’s discuss the potential limitations and importance, and ways to put together a balance between the significance and constraints of fracking.
Potential Constraints and Risks due to Hydraulic Fracturing
Though fracking is designed to extract natural gas as a way to reduce carbon print and greenhouse gas emission; it comes with its own limitations.
The amount of water required for fracking on an average is 8 million liters, which is equivalent to the daily consumption of 65000 people in the US.
Chemicals like Benzol and Formic acid used during the fracking process highly contaminates the water used. This is referred to as wastewater or flow back water or produced water. The wastewater reportedly contains massive amounts of brine (salts), toxic metals, and radioactivity, that it cannot be treated in a wastewater treatment plant.
Almost 60-80% of wastewater remains underground. As fracking wastewater is contaminated and radioactive, they need to be properly treated for disposal. This disposal of this wastewater is done either by transporting to disposal locations or storing the wastewater deep under the earth in thick concrete containers.
Surface water contamination through spillage and improperly built and maintained waste pits or tailing ponds great threat to irrigation and farming.
Apart from water prone risks, fracking also causes air pollution and poses great climatic change threats as methane – one of the greenhouse leaders is released in enormous amount during the process.
Improper concretion or spillage of wastewater deep underground can cause earthquakes. China has recently faced an earthquake due to the fracking boom on Feb 24.
Poses great health hazards borne to air pollution. Forbes study states that Babies born within a 3 kilometers radius of a fracking site are more likely to suffer from poor health.
“Countries such as Scotland have placed a temporary moratorium on the practice due to risk concerns and strong public opposition whereas it is banned in many states of Australia and completely in France.”